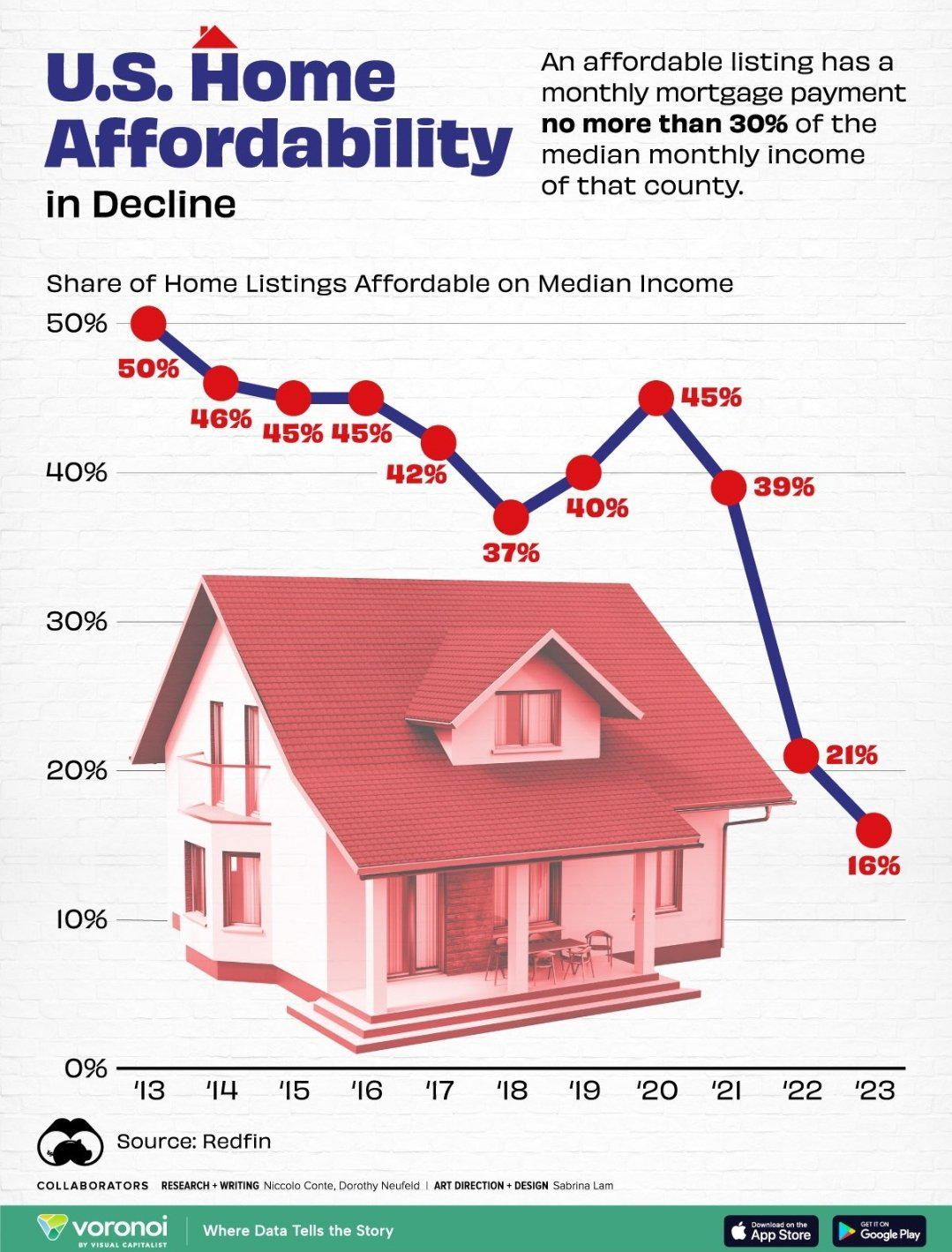
The housing affordability crisis has become a pressing issue in the United States, as skyrocketing home prices leave many struggling to realize the dream of homeownership. Over the past few decades, the cost of new single-family homes has more than doubled, driven by a combination of rising labor and material costs and stricter land-use regulations. NIMBY policies have stifled construction productivity, impeding builders from meeting the growing demand in the housing market. These restrictive measures not only limit the size of proposed developments but also exacerbate homeownership challenges faced by many Americans. As the construction sector grapples with these challenges, a closer look reveals how rethinking land-use policies could foster more affordable housing solutions and rejuvenate productivity in this critical industry.
The ongoing crisis in housing affordability—often highlighted by escalating home prices and restricted access to ownership—points to deeper systemic issues within the construction sector. Various factors have contributed to this dilemma, including increased land-use regulations and the prevalence of NIMBY attitudes that hinder development efforts. As smaller scale projects dominate the landscape, the construction industry’s productivity has stagnated, complicating the quest for affordable living options. Challenges in securing stable, equitable housing solutions have widespread implications for society, from economic stability to community growth. Addressing these intertwined issues might create pathways to revitalizing the housing market and rebuilding the promise of homeownership for future generations.
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis in the United States represents a multifaceted issue that has escalated over the decades. With home prices rising at an unprecedented rate, many Americans find themselves priced out of homeownership. This crisis is exacerbated by various factors, including soaring construction costs, stringent land-use regulations, and shrinking inventories of affordable housing. As the gap widens between income growth and housing costs, the dream of owning a home is becoming increasingly elusive for many individuals, particularly younger generations.
Additionally, local governments often impose strict land-use regulations that can prevent developers from building the affordable housing that is greatly needed. These policies typically stem from NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) sentiments, which reflect community preferences to maintain certain neighborhood characteristics. Unfortunately, such regulations not only limit the supply of new housing but also contribute to skyrocketing prices, placing further strain on potential homebuyers and renters trying to navigate this complicated housing market.
The Influence of NIMBY Policies on Construction Productivity
NIMBY policies significantly affect construction productivity in the housing sector, as they create barriers that inhibit development. Such regulations often require lengthy approvals and can complicate the construction process, leading to increased costs and delays. Builders are forced to adapt to a myriad of local requirements and homeowner associations, instead of striving for economies of scale that could reduce housing prices. This has led to a marked decrease in large-scale housing projects which historically allowed for mass production of homes.
Furthermore, the increase in land-use regulations after the 1970s has seen construction firms become smaller and less productive. With smaller projects, builders lack the resources to innovate and invest in more efficient construction methods, resulting in stagnant productivity levels within the industry. As a consequence, the overall construction productivity has stagnated in contrast to other sectors of the economy, making it evident that NIMBY policies significantly obstruct the pathways to unhindered and efficient housing development.
Land-Use Regulation and Its Impact on the Housing Market
Land-use regulation plays a pivotal role in shaping the housing market dynamics. While these regulations are often instituted to protect residential neighborhoods and promote orderly development, they inadvertently contribute to the diminished availability of housing. Many areas enforce limits on the size and density of residential projects, which stifles the potential for community growth and increases home prices. The history shows a stark correlation between rising regulations and decreasing construction productivity, further complicating the housing affordability crisis.
Moreover, as the regulatory environment tightens, builders are restricted in their ability to create diverse and affordable housing options, thus disproportionately affecting lower-income individuals. The struggle for affordable housing is emblematic of the larger issues of economic inequality and access to homeownership. Consequently, revisiting and reforming land-use regulations may be essential to alleviate some of the pressures built up in the housing market, enabling builders to create more accessible and affordable homes.
Homeownership Challenges Facing Millennials and Future Generations
Homeownership challenges are particularly acute for millennials and younger generations, who face a perfect storm of high housing costs, student debt, and stagnant wages. With housing prices more than doubling since 1960, many young professionals are left with limited options as they struggle to secure a foot in the door of the housing market. This demographic often has to contend with the financial reality of skyrocketing rents which, in many urban areas, can consume a significant portion of their income, making it difficult to save for a home of their own.
The declining rates of homeownership among younger Americans reflect not just economic challenges, but also the systemic barriers in the housing market. Policies that favor existing homeowners contribute to an environment where new entrants are pushed aside. As young people delay homeownership, the long-term implications for wealth accumulation and economic stability are concerning. They are often left to navigate a landscape where investment in real estate feels increasingly unattainable.
The Economic Consequences of Housing Market Stagnation
The stagnation in the housing market, fueled by a myriad of factors including NIMBY policies and rising construction costs, has wide-ranging economic consequences. When homeownership declines, not only do individuals miss out on wealth-building opportunities, but it also puts a strain on overall economic growth. Homeownership is a significant driver of consumer spending; when people cannot invest in their own property, they tend to invest less in local economies, which can hinder job creation and economic revitalization.
Additionally, the construction sector plays a crucial role in the broader economy. A decline in building projects can lead to reduced employment opportunities within the construction industry, stunting innovation and productivity. This shift can hinder progress in related sectors such as manufacturing and servicing, ultimately affecting the resilience and adaptability of the economy as a whole. To stimulate growth, broad policy changes focusing on the housing sector could help reignite the economy and provide pathways towards increased homeownership.
Promoting Innovation in the Construction Sector
To address the housing affordability crisis and enhance construction productivity, it is crucial to foster innovation within the construction sector. Embracing new technologies and techniques can reduce overall costs, making housing more accessible. This could include the adoption of modular construction practices that allow for faster and more efficient building processes or the integration of sustainable materials that reduce environmental impact while minimizing costs.
Moreover, encouraging collaboration between developers, policymakers, and community members can lead to innovative solutions to housing challenges. By moving toward adaptive regulatory frameworks that support creative project designs and large-scale initiatives, communities can alleviate some restrictions imposed by NIMBY sentiments. Such collaborations could create a pathway for high-quality and affordable homes to be built, ultimately benefiting the local economy and the housing market.
Reforming Housing Policies to Encourage Growth
Reforming housing policies is essential for promoting growth and mitigating the housing affordability crisis. Streamlining approval processes for new housing developments can significantly increase the speed and efficiency of construction projects. Additionally, reducing overly stringent zoning regulations can open up opportunities for diverse housing types, thus catering to the varied needs of communities. By fostering a pro-development environment, cities can combat the detrimental effects of NIMBYism.
Furthermore, implementing policies that incentivize the construction of affordable housing can help bridge the gap for low to middle-income individuals seeking homeownership. Such measures could include tax breaks for developers who create affordable units or subsidies for first-time homebuyers. By aligning policy goals with the pressing demands of the housing market, governments can ensure that all residents have access to equitable homeownership opportunities.
The Role of Local Governments in Addressing the Crisis
Local governments play a crucial role in addressing the housing affordability crisis through their policies and land-use plans. Their decisions directly influence the amount and type of housing available in communities. By prioritizing housing development and creating comprehensive plans that incorporate affordable options, these governments can stimulate growth and cater to citizens’ needs. Effective communication with residents can help ease NIMBY concerns while focusing on the broader community’s well-being.
Moreover, local governments can leverage public-private partnerships to increase the variety of housing options available. Collaborating with developers can lead to innovative solutions that balance community desires with the pressing need for new housing. These partnerships can also foster investments in infrastructure, which is essential for making neighborhoods more attractive to potential homeowners, thereby alleviating the pressures of the housing market.
Long-Term Solutions for Sustainable Homeownership
Finding long-term solutions for sustainable homeownership requires addressing the root causes of the housing crisis. Developing a nationwide strategy that encompasses both urban and rural areas could facilitate a more balanced distribution of housing opportunities. This includes considering the desires of communities while simultaneously working towards enhancing housing supply. The commitment to creating diverse and accessible housing options will be key to fostering a viable path for future homeowners.
Additionally, it is essential to incorporate financial education programs that empower prospective homeowners with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate their options effectively. By clarifying the homebuying process and available financial assistance, communities can better equip individuals and families to make informed decisions. Investing in sustainable housing initiatives can provide enduring solutions that meet the community’s needs while encouraging homeownership growth.
Evaluating the Future of the Housing Market
Evaluating the future of the housing market involves looking at trends, challenges, and potential solutions that will shape the landscape in the coming years. As the nation continues to grapple with a housing affordability crisis, understanding the shifts in demographics, economic patterns, and legislative changes will provide insights into where the market is headed. Millennials, along with Generation Z, represent a substantial portion of homebuyers, creating new demands and expectations around housing.
Given the current trajectory, the housing market must adapt to meet the needs of these groups, which include a preference for sustainable, affordable, and well-located housing. A critical part of this evaluation will involve rethinking land-use policies that have historically favored restrictive practices. Encouraging a diverse range of housing options and prioritizing developments that create community-wide benefits can enable the housing market to thrive and evolve positively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NIMBY policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY, or ‘Not In My BackYard,’ policies play a significant role in the housing affordability crisis. These policies often lead to strict land-use regulations that limit housing development, reducing the number of homes available in desirable areas. As a result, builders face challenges in creating affordable housing options, leading to increased prices and homeownership challenges for many Americans.
What impact does land-use regulation have on the housing market and affordability?
Land-use regulations can severely limit construction projects, contributing to the housing affordability crisis. By imposing restrictions on density, project size, and types of homes that can be built, these regulations hinder large-scale developments. Consequently, with fewer homes available and high demand, prices soar, making homeownership increasingly unattainable for many.
In what ways does construction productivity affect the housing affordability crisis?
Construction productivity directly affects the housing affordability crisis. As productivity declines due to restrictive land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, fewer homes can be built efficiently, leading to higher costs. The reduced ability of builders to leverage economies of scale leads to smaller and more expensive homes being developed, making homeownership out of reach for many Americans.
What are the main homeownership challenges caused by the housing affordability crisis?
The housing affordability crisis presents several homeownership challenges, including skyrocketing home prices, rising mortgage rates, and stringent lending practices. These challenges disproportionately affect low- and middle-income families, making it difficult for them to save for down payments and ultimately own homes in the current housing market.
How does the decline in large-scale building projects impact housing prices?
The decline in large-scale building projects exacerbates the housing affordability crisis by limiting the supply of homes. When projects are smaller due to land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, it leads to less efficient construction, resulting in higher prices per unit. This limited supply drives up competition among buyers, increasing prices overall in the housing market.
What role does innovation play in addressing the housing affordability crisis?
Innovation is crucial in addressing the housing affordability crisis as it can lead to more efficient building methods and cost-effective housing solutions. However, the decline in construction productivity and patenting activity in the housing sector suggests that innovation has stagnated. Encouraging new technologies and practices in construction could help reduce costs and improve housing availability.
Why is the construction sector’s productivity lagging compared to other industries?
The construction sector’s productivity is lagging due to several factors, including rigid land-use regulations and increased NIMBYism. These constraints hinder the ability of builders to operate at scale and implement innovations seen in other industries, leading to fewer homes being built and ultimately contributing to the housing affordability crisis.
How can we combat the housing affordability crisis caused by NIMBY policies?
Combating the housing affordability crisis requires re-evaluating NIMBY policies that restrict housing development. Implementing more flexible land-use regulations, encouraging larger-scale projects, and fostering a collaborative approach with communities can help increase housing supply and make homeownership more accessible for a broader range of people.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The housing affordability crisis stems from rising costs and complicated regulations |
| Productivity in construction has decreased significantly since 1970 due to land-use regulations |
| NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies prevent large-scale developments that could alleviate housing shortages |
| Large builders are more efficient than smaller firms, yet their market presence has dwindled because of regulatory burdens |
| Intergenerational transfer of housing wealth shows that young Americans are increasingly locked out of home ownership |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a growing concern in America, driven by a combination of rising costs, regulatory hurdles, and insufficient large-scale housing projects. This situation not only impacts the ability of many Americans to purchase homes but also reflects a wider trend of wealth concentration among older generations, leaving millennials and younger individuals struggling to secure affordable housing. Addressing these challenges requires a reevaluation of current land-use regulations and a concerted effort to foster innovation within the construction sector.