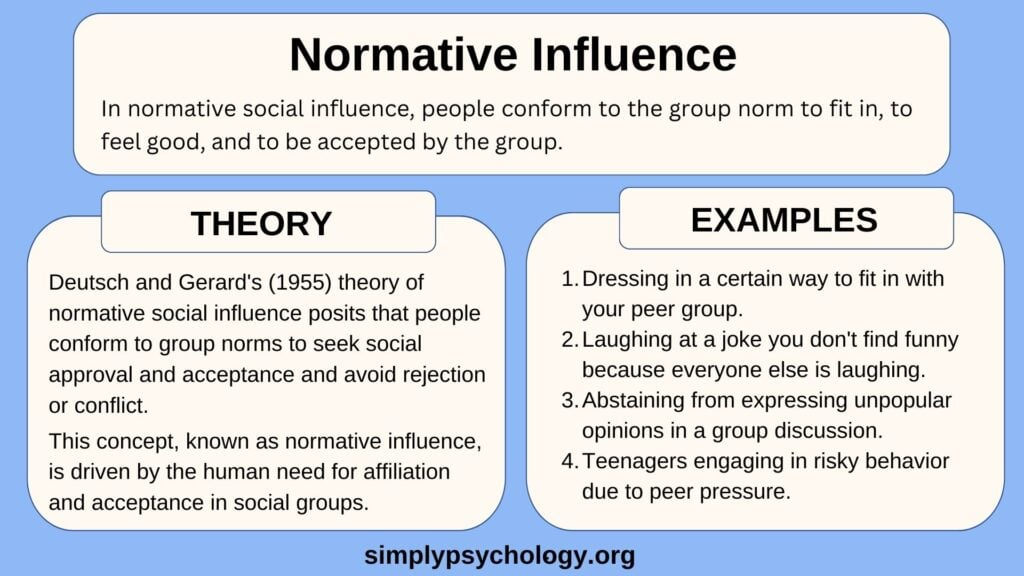
The influence of social norms on preferences plays a significant role in shaping our choices and attitudes. Behavioral scientists suggest that what we like often stems from the societal standards and cultural influences around us, highlighting how interconnected our decisions truly are. For instance, our preference formation is not just a solitary journey but rather a communal experience where family traditions, peer groups, and even social media impact consumer behavior significantly. When we consider how social influence choices affect what we deem desirable, it becomes clear that our likes and dislikes are frequently curated by external factors rather than purely personal taste. Understanding this dynamic not only enhances our grasp of our own consumer behavior but also sheds light on the broader implications of societal trends on individual preferences.
Exploring the dynamics of choice in contemporary life reveals much about how collective attitudes shape individual tastes. The interplay between societal expectations and personal inclinations can often dictate what we find appealing, from fashion trends to favorite foods. This phenomenon, recognized in behavioral science, underscores that many of our preferences are constructed rather than innate. Social influences, whether through friends, family, or media channels, help form our likes and dislikes, making them more a reflection of the communities we inhabit than a straightforward representation of our identity. Thus, examining how social norms operate offers insightful perspectives on the mechanisms behind our decision-making processes.
Understanding Consumer Behavior: Social Influences on Preferences
Consumer behavior is often shaped more by social influences than individuals may realize. Studies in behavioral science highlight that our preferences can be largely informed by the choices of those around us. Social norms play a critical role in consumer behavior; for instance, when shopping for products, individuals are likely to gravitate towards brands that are popular within their social circles. This phenomenon suggests that we are not as autonomous in our choices as we believe, but rather, we are influenced by a complex web of social interactions and cultural contexts.
Moreover, our preferences are often formed in reaction to social influences that extend beyond mere peer pressure. This can include familial preferences, as seen in how children often adopt similar tastes in products, such as the type of music they listen to or the foods they consume. For example, a person might favor a specific spaghetti sauce because it was routinely served in their household growing up. This connection illustrates that our preferences are deeply rooted in social norms and shared experiences, challenging the notion that our likes are entirely personal.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do social norms influence individual preferences in consumer behavior?
Social norms significantly shape consumer behavior by setting expectations on acceptable choices and trends. These norms can determine what products are popular and influence individuals to conform to group preferences, often subconsciously. As people seek acceptance within their social circles, they may gravitate toward brands that resonate with prevailing social attitudes, thus forming their preferences in line with the community.
What role do attitudes play in the formation of preferences influenced by social norms?
Attitudes can both influence and be influenced by social norms. When individuals adopt preferences endorsed by their social groups, their attitudes toward these products can evolve. For example, someone may initially be neutral about a specific brand but start to prefer it after observing peers’ positive attitudes toward it. This reciprocal relationship highlights how social norms affect the formation of preferences.
Can social influence lead to changes in personal preferences over time?
Yes, social influence is a powerful force that can lead to changes in personal preferences over time. As individuals interact within their social environments, exposure to new ideas and collective choices can shift their preferences. For instance, a person may enjoy a type of music or food that they previously had no interest in simply because their friends or community embrace it.
How do social norms affect preferences in product choices among different demographic groups?
Demographic groups often exhibit distinct product preferences shaped by social norms rooted in culture, age, and societal values. For example, younger consumers might lean toward brands that emphasize sustainability due to prevailing social attitudes in their peer groups. In contrast, older demographics might prefer established brands with a history that aligns with their experiential preferences, demonstrating how social influence varies across different segments.
What are some examples of how social norms shape our preferences in daily life?
Social norms shape preferences in various ways, such as brand choices influenced by peer behaviors, fashion trends dictated by social media, and dietary habits stemming from communal practices. For instance, if a group of friends regularly dines at a particular restaurant, individuals within that group may develop a preference for its cuisine, illustrating the impact of social influence on daily choices.
How can understanding social influence help marketers target consumer preferences effectively?
Understanding social influence allows marketers to craft strategies that resonate with targeted consumer segments. By recognizing the norms and behaviors prevalent among their audience, marketers can tailor messages and product placements that align with societal expectations and preferences, effectively utilizing social proof to boost product appeal and acceptance.
In what ways can individuals resist social norms when forming their preferences?
Individuals can resist social norms by cultivating awareness of external influences and making conscious choices that align with their unique values. By actively seeking diverse perspectives, experimenting with new products, and reflecting on personal needs, individuals can form authentic preferences that may diverge from prevailing social norms, thereby asserting their individuality.
Can the influence of social norms on preferences lead to a homogenization of consumer choices?
Yes, the influence of social norms can result in a homogenization of consumer choices. As individuals conform to collective preferences, distinctiveness in choices may diminish, leading to a prevalence of similar product selections across populations. This phenomenon often manifests in trending products that achieve widespread popularity due to social validation, overshadowing more diverse or niche options.
What is the relationship between social influence and preference formation in behavioral science?
In behavioral science, the relationship between social influence and preference formation is intricate. Social influence often dictates the information individuals receive, impacting their choices and preferences. Preferences can be shaped not just by personal experiences but also by the shared behaviors and endorsements within one’s social network, leading to a complex interplay between individual identity and group dynamics.
How do generational differences impact the influence of social norms on preferences?
Generational differences can greatly impact the influence of social norms on preferences. Younger generations may prioritize sustainability and social justice, while older generations might focus on brand loyalty and reliability. These differences illustrate how varying social norms across generations shape unique preferences in consumer behavior, resulting in diverse market demand and product development strategies.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Influence of upbringing | Parents’ preferences heavily shape children’s tastes and choices. |
| Development of preferences | Musical tastes are often formed during adolescence, while other preferences develop in response to specific needs (like shopping for a car). |
| Choice and attitude relationship | Our attitudes affect our choices, but often our choices shape our attitudes as well. |
| Social Media’s Role | Social media reflects our identities and influences our preferences through targeted ads. |
| Preference formation and AI | AI helps identify hidden associations in data, leading to more personalized marketing strategies. |
| Cultural Variance | Preferences may vary significantly across cultures, yet common choices may emerge globally (e.g., water brands). |
| Switching costs in preferences | Switching brands or preferences can vary in difficulty; high-switching costs lead to more consistent choices. |
Summary
The influence of social norms on preferences is profound and often subconscious. Our likes and dislikes are not solely products of personal taste; they are significantly shaped by our upbringing, the immediate environment, and societal cues. Understanding this influence reveals that preferences are not merely individual choices but are intricately woven into the fabric of societal interactions and norms. From our childhood experiences with family to the tailored advertisements we encounter on social media, these factors collectively mold our consumer behavior and social identities. Recognizing the impact of these social norms can lead to deeper insights into how we express ourselves and make choices in our daily lives.