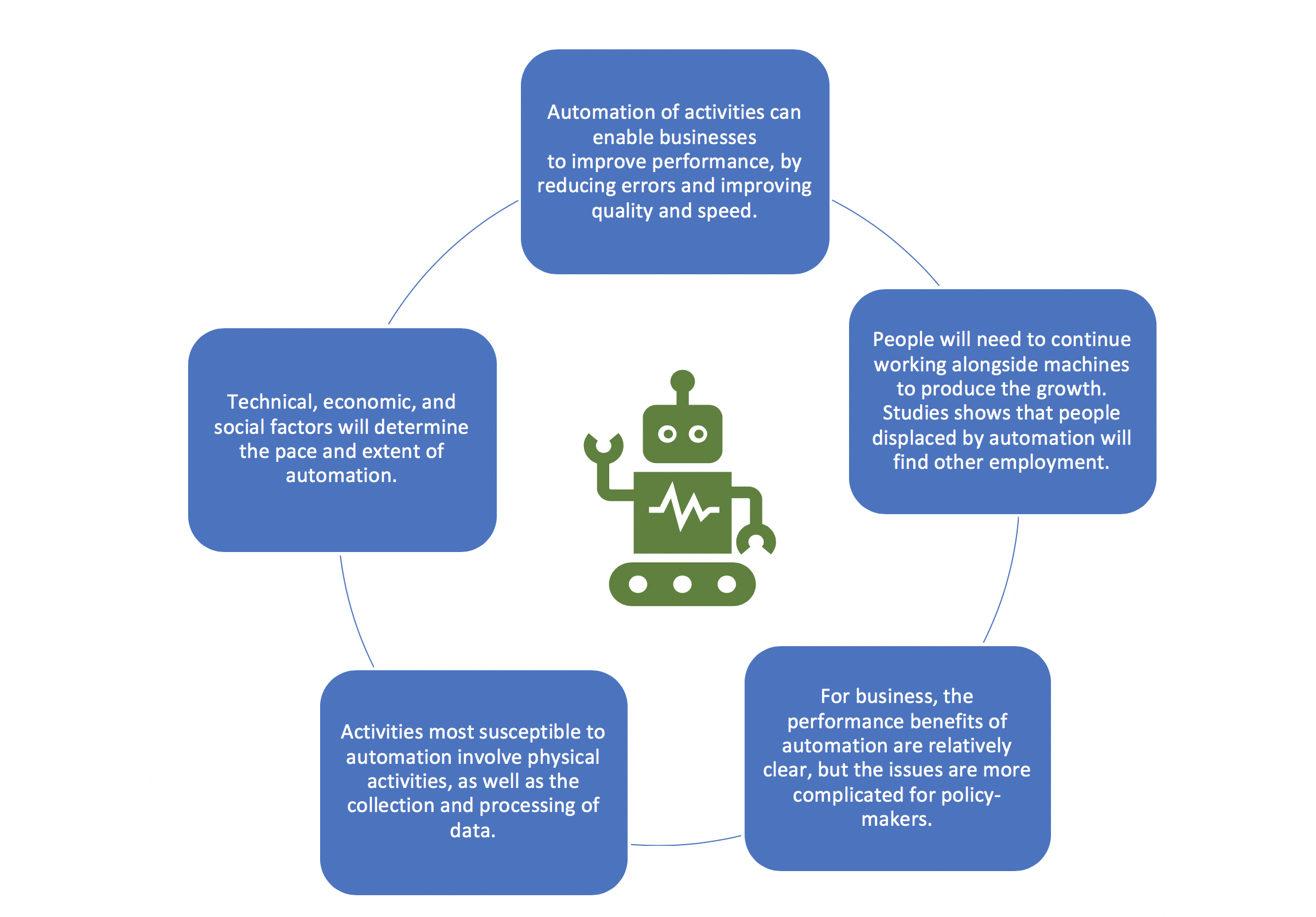
The impact of AI on the labor market is a pressing topic that has piqued the interest of economists and policymakers alike. Recent studies reveal that this transformative technology is set to reshape employment landscapes in unforeseen ways, resulting in both challenges and opportunities. While automation and AI promise efficiency and innovation, they may also contribute to significant labor market trends, such as occupational churn and economic disruption. These changes could redefine job security and workforce skills, compelling many to adapt to an evolving set of demands. As research suggests, understanding AI and jobs becomes critical for navigating the future of employment in an increasingly automated world.
The influence of artificial intelligence on employment dynamics is becoming increasingly significant, prompting discussions around workforce evolution and the future of work. This phenomenon, sometimes referred to as technological advancement in the job sector, is steering substantial changes within the economy. Historical analyses show how breakthrough technologies have led to fluctuating labor market patterns, exposing workers to both new opportunities and displacement risks. The evolving landscape of job sectors reflects a broader trend of occupational shifts, where traditional roles are disrupted, necessitating new skill sets and adaptability. Thus, grappling with technology and employment implies a need for businesses and individuals to rethink strategies for a more resilient workforce.
The Changing Face of the Labor Market
The evolution of the labor market over the past century reflects significant technological advancements, particularly in AI and automation. With historian David Deming’s research, we see the relationship between occupational churn and tech disruption more vividly than ever. This historical perspective reveals that while there were stable periods, the onset of AI is bringing forth a new wave of change that influences job availability and occupational dynamics. As the nature of work shifts, understanding these trends becomes crucial for both employees and employers.
In recent years, the labor market has experienced an increasing emphasis on high-skilled positions, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). This shift hints at a demand for job roles that not only require advanced training but also the dexterity to work alongside emerging technologies. As AI integrates into various industries, the labor landscape is primed for a transformation that could lead to diminished roles in lower-skilled jobs and, conversely, an explosion of opportunities in tech-driven fields.
AI and Its Impact on Labor Market Trends
The influence of artificial intelligence on the labor market is profound, shifting the way job roles are defined and executed. Recent studies indicate that AI has led to an increase in both the demand for skilled workers and an unsettling decline in low-paid service positions. This shift aligns with the concept of occupational churn, as jobs evolve and new fields emerge, driven primarily by technological innovation. With the rapid pace of AI development, employees across all sectors should remain aware of how these technologies could redefine their job roles.
AI’s impact extends beyond just job creation; it also reshapes existing professions, making adaptability crucial for today’s workforce. As traditional roles evolve, workers find themselves needing advanced skills to remain relevant. This scenario underscores the necessity for ongoing education and training, as the AI revolution requires a workforce that can harness technology rather than compete against it. The challenge lies in navigating this transformation, where the economic disruption caused by AI could lead to significant shifts in labor market trends.
Occupational Churn and Economic Disruption
Understanding occupational churn – the constant movement of labor among different jobs – is key to comprehending the labor market’s volatility. Deming’s analysis reveals how technological advancements trigger significant shifts, causing certain sectors to thrive while others decline. The rise of AI is indicative of this phenomenon, as it disrupts traditional employment structures, pushing workers toward new skill sets and job opportunities. The historical data highlights that such changes have occurred before, although the current rate of change driven by AI is unprecedented.
As we analyze the effects of economic disruption on the labor market, it becomes clear that the dynamic is not merely cyclical but transformative. Industries reliant on manual labor are under threat, while sectors that embrace technology see growth. This discrepancy poses a challenge for employees in lower-skilled positions who face potential displacement. It emphasizes the need for workforce development and supportive measures to transition affected workers into roles that reflect the evolving demands of an AI-driven economy.
The Rise of STEM Jobs in an AI-Driven Economy
The growing influence of AI has sparked a resurgence in demand for STEM jobs, highlighting a significant shift in employment patterns. As industries increasingly integrate data-driven technologies, roles like software developers and data analysts have surged from 6.5% to nearly 10% of the labor market between 2010 and 2024. This nearly 50% increase underscores the necessity for educational systems to evolve and prepare students for the future workforce that’s heavily reliant on technological aptitude.
Moreover, the expansion of STEM jobs showcases a broader trend towards specialization in the labor market, where professionals are not just expected to perform tasks but also innovate and adapt to new tools. Companies are investing heavily in AI-enhanced technologies, driving demand for proficient workers who can leverage these advancements. For current and future job seekers, focusing on STEM fields offers a pathway to security in a labor market that is continuously shaped by technological innovation.
Navigating Labor Market Volatility
Labor market volatility is an inherent challenge, especially as we grapple with rapid technological change driven by AI. The findings from Deming and Summers suggest that the labor market is not just experiencing job shifts but rather a transformative process that alters the job landscape itself. Workers must remain vigilant and adaptable, continuously improving their skills to align with new market demands. The capacity to pivot in response to shifting trends will determine individual success in an increasingly competitive environment.
As economic disruption unfolds, it’s vital to address the needs of displaced workers and facilitate a smoother transition into emerging job markets. Initiatives, such as targeted retraining programs and support networks, can assist those affected by labor market shifts. As we witness the convergence of technology and employment, ensuring access to education and training becomes paramount in safeguarding the workforce against volatility while preparing for future opportunities rooted in innovation.
The Potential Displacement of Low-Paid Jobs
The emergence of AI technologies has raised concerns about the future of low-paid jobs, particularly in the service sector. As data suggests, the overall share of employment in these areas has seen a decline since 2019, a trend indicative of automation’s growing role. This shift brings to light the harsh reality that many lower-skilled positions are at risk of obsolescence as companies adopt AI solutions to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs.
The looming question for policymakers and labor advocates is how to support individuals in low-paid roles as the job landscape changes. While some positions may return as the economy stabilizes, evidence points to a reduced demand for roles that are easily automated. Strategies must focus on empowering affected workers with skills that translate into higher-paying and more sustainable employment opportunities, highlighting the importance of embracing educational reforms to facilitate this transition.
Adapting to Technology and Employment Trends
Adapting to the intersection of technology and employment is essential for both job seekers and organizations alike. As we witness the integration of AI into various sectors, the need for resilience and adaptability in the workforce becomes increasingly clear. Workers must cultivate a mindset geared towards lifelong learning, recognizing that engaging with new technologies is vital for career longevity. Employers, on the other hand, must foster an environment that encourages continuous skill development and embraces innovation within their teams.
Moreover, organizations should invest in training programs that not only address current skill gaps but also anticipate future industry needs. By integrating technological training into their workforce development strategies, businesses can prepare for the inevitable changes that AI will continue to bring to the labor market. The collaborative effort between individuals and organizations is crucial for navigating these transformative times and seizing the opportunities that arise from technological advancement.
Forecasting the Future of Work
Looking ahead, it is essential to forecast how AI will shape the future of work. As suggested by Deming and Summers, we may not only see a careful reallocation of jobs but also the creation of new industries that didn’t exist prior to the AI revolution. With technological advancements constantly evolving, the labor market is poised for continuous transformation. This scenario presents both challenges and opportunities for workers as the definition of job roles redefines itself.
Navigating this future requires proactive engagement from all stakeholders involved in the labor market. Whether it’s industry leaders, educational institutions, or government bodies, there is a collective responsibility to create pathways to equip future generations with the skills they need. A well-prepared workforce will ensure that the benefits of AI and technological progress are distributed equitably, ultimately shaping a resilient economy that fosters innovation while minimizing disruption.
The Role of Knowledge Workers in an AI Landscape
In an increasingly automated world, the role of knowledge workers is set for significant evolution. As AI technologies automate various tasks traditionally performed by humans, those working in sectors such as finance, journalism, and management must adapt to meet heightened performance expectations. The intersection of automation and productivity will challenge professionals to become not just users of technology but also innovators who leverage these tools to enhance their output.
Automation may indeed bring about temporary increases in productivity, but it also signals a deeper shift in job roles for knowledge workers. As companies begin demanding more from their employees, especially during economic downturns, it’s imperative for knowledge workers to embrace continuous improvement and technological literacy. This transition will be crucial in ensuring they remain competitive and relevant in a rapidly changing landscape that values efficiency and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of AI on the labor market trends today?
AI is significantly impacting labor market trends by increasing demand for high-skilled jobs, particularly in STEM fields. As companies invest in AI and related technologies, there’s a notable shift towards well-compensated positions while low-paid service jobs experience decline. This emergence of AI as a crucial factor indicates a transformation towards a more tech-driven economy.
How does AI contribute to occupational churn in the labor market?
AI contributes to occupational churn by reshaping job distribution across various industries. The study reveals that while some sectors experience growth due to AI, others, particularly low-paid service jobs and retail sales, face sharp declines. This dynamic showcases the volatility of the labor market as technology evolves and alters employment needs.
Are AI and jobs becoming a threat to the existing labor market?
AI and jobs are creating both opportunities and threats in the labor market. While AI enhances productivity and creates new roles, it also poses risks of job displacement, particularly in low-skilled sectors. Knowledge workers need to adapt quickly, as firms increasingly expect more productivity from staff, influenced by advancements in AI.
What is meant by economic disruption in relation to AI and the labor market?
Economic disruption refers to the significant changes and instability caused by AI in the labor market. As AI technologies emerge, they disrupt traditional job roles, leading to a reallocation of positions and skills required. This disruption can result in both job creation in tech-heavy fields and job losses in sectors unable to adapt.
How has AI changed employment patterns over the last century?
AI has altered employment patterns by fostering volatility in job sectors historically stable for many years. Recent findings suggest that since 2019, occupations are changing rapidly as AI-driven technologies come to the forefront, emphasizing the need for workforce adaptability to remain relevant in a tech-centric job market.
What trends are emerging from AI’s influence on the U.S. labor market?
Emerging trends from AI’s influence on the U.S. labor market include a rise in STEM job opportunities, a stark decline in low-paid service jobs, and an overall restructuring of employment sectors favoring high-skilled positions. As firms adopt AI, there’s a notable shift in workforce demands, pushing for more specialized skills.
Is AI responsible for job losses in retail and service sectors?
AI is partially responsible for job losses in retail and service sectors as it streamlines operations and boosts e-commerce growth, reducing the need for traditional retail roles. The study indicates that with the rise of online shopping and AI usage, many of these low-skilled job positions are unlikely to return.
What does the term ‘job polarization’ mean in the context of AI’s effect on the labor market?
Job polarization refers to the growing disparity in job opportunities across different wage levels, where high-skilled, well-paying jobs increase, while middle-income roles diminish. In the context of AI, this polarization highlights a shift towards demand for highly trained workers, leaving lower-skilled positions vulnerable to displacement.
How should workers prepare for the changes AI brings to the labor market?
Workers should prepare for changes brought by AI by focusing on upskilling and reskilling in technical areas relevant to their fields. Emphasizing adaptability and continuous learning will be crucial as AI-driven advancements reshape job expectations and requirements across various sectors.
What role does STEM education play in the evolving labor market influenced by AI?
STEM education plays a critical role in the evolving labor market influenced by AI, as there is a growing demand for professionals in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields. As AI technologies become integral to more industries, a strong STEM education can provide the necessary skills for emerging job opportunities.
| Key Points |
|---|
| A study by David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers reveals how AI is influencing the U.S. labor market. |
| Historically, technology brought stability from 1990 to 2017, contradicting fears of job loss due to automation. |
| Post-2019, a significant shift in job trends attributed to AI and other technologies has been observed. |
| AI is linked to an increase in high-paying, highly-skilled jobs while low-paid service jobs are declining. |
| The rise of STEM jobs is notable, expanding from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024—an almost 50% increase. |
| Retail sales jobs have drastically decreased due to online shopping behavior prompted by the pandemic and AI. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as studies show significant shifts in job trends and employment dynamics. Economists have identified several pivotal trends, including the rise of high-skilled jobs and the decline of low-paid positions, especially in retail and service sectors. Current evidence suggests that while AI helps create opportunities, it concurrently poses risks of job displacement in various industries, demanding a re-evaluation of workforce skills and job roles as we advance further into the digital age.